In our day, energy and the efficient use of energy are among the most important factors, and the main purpose of use of pre-insulated pipes is to keep heat loss at the lowest possible level and obtain the highest efficiency from energy. The calculation method given below can be used for calculating the heat loss theoretically.
First of all, the average fluid temperature is calculated:
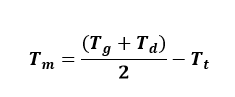
Tm (˚C) : Average temperature of the fluid
Tg (˚C) : Temperature at the direction of flow
Td (˚C) : Temperature at the direction of return
Tt (˚C) : Outdoor air temperature
In order to calculate the total thermal conductivity resistance of the pre-insulated pipe system, firstly the resistances of each layer of the system must be calculated respectively.
Carrier Pipe Thermal Conductivity Resistance:
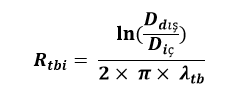
Rtbi (m.°C / W) : Thermal conductivity resistance of the carrier pipe
Din (m) : Inner diameter of the carrier pipe
Dout (m) : Outer diameter of the carrier pipe
λtb(W / m.°C) : Carrier pipe thermal conductivity coefficient (Table 1)
|
Type of the Service Pipe |
Thermal Conductivity Coefficient (W/m.˚C) |
|
Black Steel |
76 |
|
Stainless Steel |
16 |
|
PP-R |
0,15 |
|
Copper |
400 |
|
CTP |
0,31 |
|
Polyethylene |
0,43 |
Table 1: Thermal Conductivity Coefficient by Types of Carrier Pipe
Polyurethane Insulation Thermal Conductivity Resistance:
Rpur= ln(DkbinDout)2× π× λpur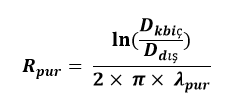
Rpur(m.°C / W) : PUR insulation thermal conductivity resistance
Dkbin(m): Inner diameter of the casing pipe
λpur(W / m.°C): PUR insulation thermal conductivity coefficient (0.026 W / m.°C can be taken)
Thermal Conductivity Resistance of the HDPE Casing Pipe:
Rkb(m.°C / W) : Thermal conductivity resistance of the casing pipe
Dkbout(m): Outer diameter of the casing pipe
Dkbin(m): Outer diameter of the casing pipe
λkb(W / m.°C): Thermal conductivity resistance of the casing pipe
Outdoor Thermal Conductivity Resistance:
- Underground Installation
Rt(m.°C / W) : Thermal conductivity resistance of earth
Z(m) : Filling height of earth
λt(W / m.°C): Thermal conductivity coefficient of earth (Table 2)
|
Type |
Density (kg/m3) |
Volumetric Humidity Rate % |
Thermal Conductivity Coefficient (W/m.˚C) |
|
Sand |
1500 |
4 |
1,04 |
|
1800 |
14 |
1,7 |
|
|
Clay Soil |
1500 |
23 |
1,5 |
|
2000 |
28 |
2,6 |
Table 2: Thermal Conductivity Coefficient of Earth
- Ground Installation
Rtdout(m.°C / W): Outer convection resistance of the casing pipe
hair(W / m².°C): Air convection coefficient
Thermal Conductivity Resistance between Flow - Return Pipes
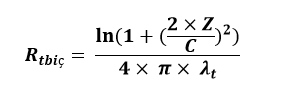
Rtbin(m.°C / W): Thermal conductivity resistance between flow - return pipes
C (m) : Distance between the axes of flow - return pipes
After calculating all resistance factors, the total thermal conductivity resistance value of the pre-insulated pipe system can be calculated through the formulas below:
- If under the ground:
- If above the ground:
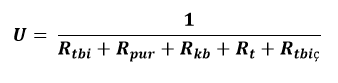
U (W/m.˚C) : Total thermal conductivity coefficient
Total heat loss per metre in pre-insulated pipes:
Q=U× To 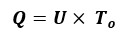
Q (W / m) : Total heat loss per metre
The formula below can be used to calculate the fluid temperature at the end of the line according to all calculations:
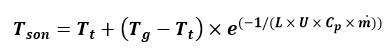
L (m) : Length of line
m (kg/sec) : Water flowrate
Cp(J / kg.°C) : Fluid specific heat [Table 3]
Tson(°C) : Fluid final temperature
|
Temperature (˚C) |
Density (kg/m3) |
Specific Heat (Kj/kg ˚C) |
|
0 |
1000 |
4210 |
|
5 |
1000 |
4204 |
|
10 |
1000 |
4193 |
|
20 |
998 |
4183 |
|
30 |
996,02 |
4179 |
|
40 |
992,06 |
4179 |
|
50 |
988,14 |
4182 |
|
60 |
983,28 |
4185 |
|
70 |
977,52 |
4191 |
|
80 |
971,82 |
4198 |
|
90 |
965,25 |
4208 |
|
100 |
957,85 |
4219 |
Table 3: Physical Specifications of Water


